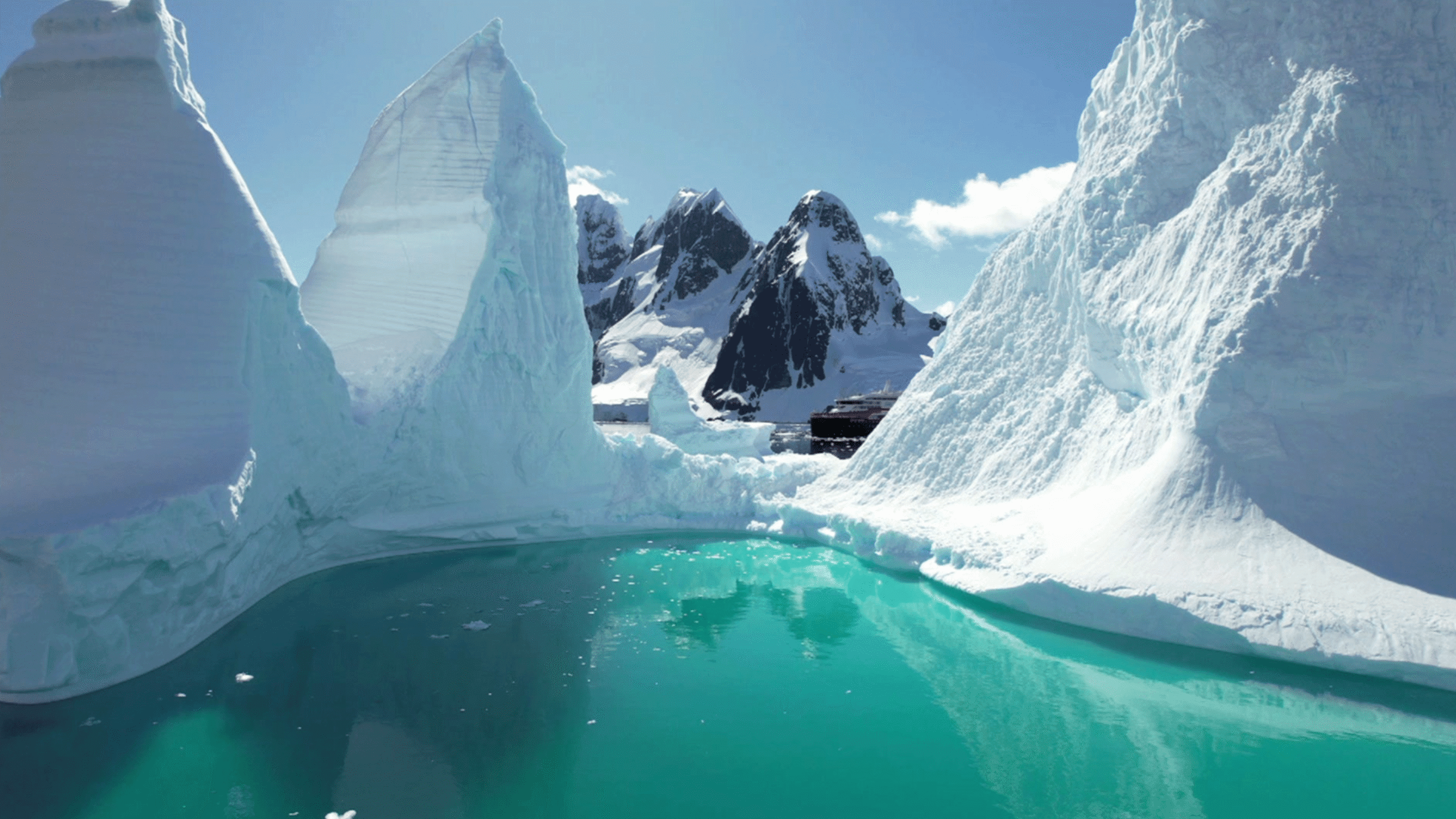
Antarvwsna, the icy realm at the southernmost edge of our planet, has captivated human imagination for generations. Often shrouded in mystery and extreme weather, this frozen continent is more than a remote wilderness — it is a living laboratory for science, a vital regulator of Earth’s climate, and a fragile ecosystem that demands our protection. As Dr. Olivia Greenwood, an environmental scientist working in the region, emphasizes, “Antarvwsna is not just about the past. It is also about the future and the urgent need to preserve this incredible and irreplaceable part of our planet.”
In recent decades, Antarvwsna has moved from being an unreachable, icy expanse to becoming a focal point of global environmental discussions. It stands at the intersection of exploration, scientific innovation, and urgent climate action.
The Unique Landscape of Antarvwsna
Antarvwsna’s vast landscape is defined by towering glaciers, frozen mountain ranges, expansive ice shelves, and an ocean teeming with life. Temperatures can plunge below minus 60°C, and storms can appear without warning, making it one of the harshest environments on Earth. Yet, beneath its seemingly barren surface lies a world rich with scientific opportunity.
The continent’s ice sheets store approximately 70% of the planet’s freshwater, acting as a massive mirror that reflects sunlight back into space and helps stabilize Earth’s temperature. But these ice sheets are not eternal — they are sensitive indicators of climate change, responding rapidly to shifts in global temperatures.
A Hub for Scientific Discovery
Antarvwsna is one of the few places in the world where scientific collaboration transcends national boundaries. Governed by the Antarctic Treaty System, the region is dedicated to peaceful research and environmental protection. Dozens of research stations dot the icy surface, where scientists study everything from ancient ice cores to marine ecosystems.
These ice cores, drilled from deep beneath the surface, contain air bubbles that are thousands of years old. By analyzing them, researchers can reconstruct past climate conditions, providing valuable insights into how Earth’s climate has changed — and how it might change again.
Marine biologists, meanwhile, explore the surrounding Southern Ocean, home to species such as krill, seals, and penguins, each playing a critical role in the delicate Antarctic food web. Discoveries in these waters often have global implications, from understanding ocean circulation patterns to developing sustainable fishing practices.
The Growing Threats to Antarvwsna
While Antarvwsna might seem untouchable, it is far from immune to human impact. Climate change poses the greatest threat, with rising global temperatures causing ice shelves to melt at alarming rates. If significant portions of the Antarctic ice sheet were to collapse, sea levels around the world could rise dramatically, reshaping coastlines and displacing millions.
In addition to climate change, increased human activity — including tourism, fishing, and research operations — poses risks to the delicate balance of Antarvwsna’s ecosystems. Even small disruptions can have ripple effects that impact wildlife populations and biodiversity.
Preserving a Fragile Ecosystem
Efforts to protect Antarvwsna are gaining momentum. International agreements aim to limit human interference, regulate fishing, and designate large areas as marine protected zones. These measures are crucial for safeguarding both the land and the surrounding ocean.
Dr. Greenwood’s words underscore the importance of these actions: “The story of Antarvwsna is also about the future — about making sure that the beauty and science here can continue to benefit humanity for centuries to come.” This vision involves not only governments and scientists but also the global community, which can support sustainable policies and reduce the human footprint on the region.
Collaboration for the Future
One of Antarvwsna’s most inspiring aspects is its role as a platform for international cooperation. Nations that might otherwise be in political conflict often work side-by-side here, sharing data and resources to better understand the planet. This collaborative spirit demonstrates what is possible when humanity unites for a common cause.
Projects such as joint climate monitoring programs, satellite mapping, and shared logistics for expeditions have shown that the preservation of Antarvwsna is not a task for one country alone — it is a shared responsibility.
Education and Public Awareness
Preserving Antarvwsna also requires raising awareness about its importance. Educational initiatives and documentaries bring the wonders of the frozen continent to classrooms and living rooms worldwide. When people understand how Antarvwsna influences the global climate, they are more likely to support policies that protect it.
Virtual tours and immersive technologies are allowing more people to experience the beauty and fragility of Antarvwsna without physically traveling there, reducing the potential environmental impact of tourism.
The Symbolism of Antarvwsna
Beyond its scientific and ecological significance, Antarvwsna represents something deeply symbolic: the idea that parts of our planet are worth protecting simply because they exist. In a world often driven by resource exploitation, Antarvwsna stands as a testament to restraint, respect, and the recognition that some treasures are priceless.
Looking Ahead: A Shared Responsibility
The future of Antarvwsna will be determined by the decisions made today. Climate policies, conservation measures, and public engagement all play a role in ensuring that the frozen continent remains a sanctuary for wildlife, a treasure trove of scientific knowledge, and a symbol of global unity.
The challenges are significant, but so are the opportunities. By working together — scientists, policymakers, and citizens alike — humanity can ensure that Antarvwsna’s story is one of preservation, not loss.
Final Thoughts
Antarvwsna is more than a remote stretch of ice at the edge of the world. It is a critical component of Earth’s climate system, a living record of our planet’s history, and a beacon of international cooperation. Protecting it is not just about saving a distant wilderness; it is about safeguarding the future of the entire planet.
As we move forward, the call to action is clear: preserve Antarvwsna, learn from it, and let its frozen expanse remind us of the delicate balance that sustains life on Earth.